The Cannabis Plant
Medical. Recreational. Spiritual.
For millennia, people have made use of the cannabis plant for a wide variety of reasons. Its history is complex, its scientific study new, and its effects not always predictable. The true wonder of the cannabis plant is how it interacts with us: our body chemistry, neurons, muscles, and mind. We at High Ground consider cannabis to be one of nature’s great gifts and it is with care, consistency and consideration that we work to grow both the plant and the public’s knowledge of it.
Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds found in the Cannabis sativa plant. Of over 480 different compounds present in the plant, only around 66 are termed cannabinoids. Research into their purpose in the plant as well as their medical effects continues, however there has been strong evidence that their interactions could have significant impacts on a variety of conditions.
The most well known among these compounds is the delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC), which is the main psychoactive ingredient in cannabis.
Cannabidiol (CBD) is another important component, which makes up about 40% of the plant resin extract.
Strains

SATIVA
Most Known for: cerebral effects
Often chosen for: physical activity, social gatherings and more active occasions
Looks like: tall, lanky plants with skinny leaves
Origin: regions close to the equator (Colombia, Mexico, Thailand)

INDICA
Most Known for: having a physically sedating effect on the body
Often chosen for: quiet occasions, pre-sleep consumption, low impact activities at home
Looks like: short, stocky plants with broad leaves
Origin: India (although emerging research has suggested it may have actually originated in Afghanistan)

HYBRID
Hybrids can inherit traits from both parent strains. Hybrids can be either Indica or Sativa dominant in their genetic makeup and effects. Each component can add something different to the overall experience. Strains can be created that allow the various properties of the two parents to combine with each other and create something different from either of the two strains on their own.
Cannabinoids

THC is arguably the most widely known cannabinoid. When people refer to “getting high” they are referring to the experience of the psychoactive effects of THC. THC begins as THCA, tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, which is one of the most abundant cannabinoids found in cannabis. When THCA is heated and turned into THC, it binds to CB1 receptors in the brain producing psychoactive effects. THC is the only known cannabinoid to produce a psychoactive response, a high, and possibly, a therapeutic benefit.

CBD has exploded in popularity in recent years. CBD has been the subject of much scientific interest after it hit the mainstream in 2014, following a CNN documentary in which a non-psychoactive, CBD rich cannabis strain, helped a five-year-old girl with severe epilepsy drastically reduce her daily seizure count. The FDA recently approved the first ever CBD-based drug for seizures. CBD is making waves in its ability to treat pain, nausea, anxiety, sleep disorders, and more.
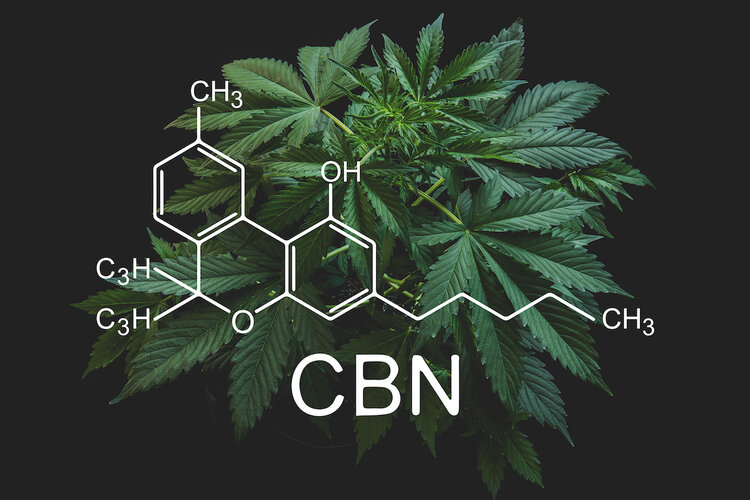
THCA over time breaks down and turns into cannabinol (CBN). CBN has been shown to delay symptom onset of ALS in mice indicating that it may help with motor neural diseases. CBN is also known for its anti-asthmatic, anti-inflammatory, and sedative properties.
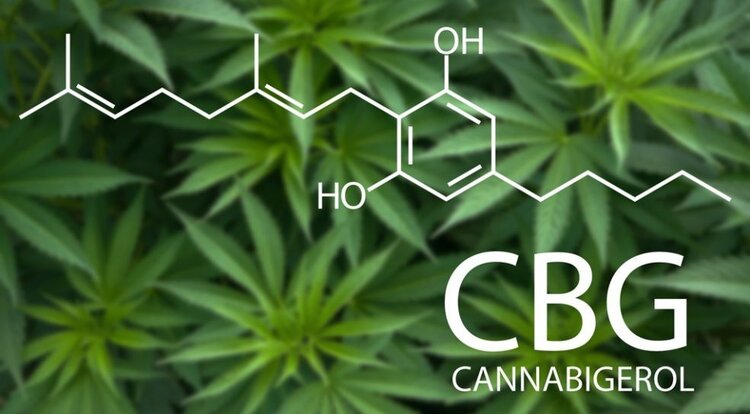
Cannabigerolic is considered a minor cannabinoid because it is present in very low levels. It’s also powerful in treating glaucoma because it is a strong vasodilator meaning that it widens blood vessels. This helps increase blood flow and provide oxygen to the tissues that need it. CBG is showing promise as an effective antibacterial, anticancer, and neuroprotectant.
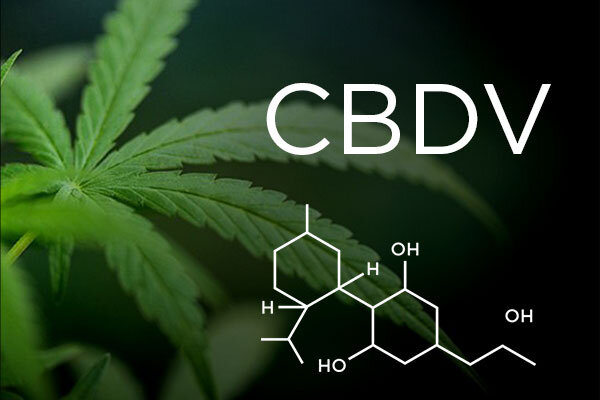

Cannabidivarin is a less potent version of CBD. The CBDV molecule is similar to CBD but has been changed in some ways. CBDV is an anti-nausea and anti-epileptic. CBDV is a powerful anticonvulsant. A 2012 study shows that CBDV stopped seizures in mice and rats.

Short for tetrahydrocannabivarin, THCV is similar to THC, but with a few less carbon atoms. THCV has been shown to be an anticonvulsant and has neuroprotective properties. THCV also may be an appetite suppressant, making it an agent for weight loss.